|
Wind is simple air
in motion. It is caused by the uneven heating of the earth’s surface by
the sun. Since the earth’s surface is made of very different types of land
and water, it absorbs the sun’s heat at different rates.
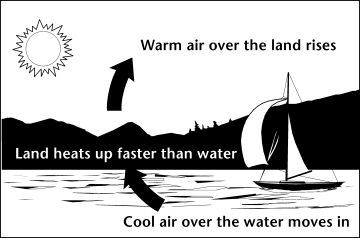
During the day,
the air above the land heats up more quickly than the air over water. The
warm air over the land expands and rises, and the heavier, cooler air
rushes in to take its place, creating winds. At night, the winds are
reversed because the air cools more rapidl y over land than over water.
In the same way,
the large atmospheric winds that circle the earth are created because the
land near the earth's equator is heated more by the sun than the land near
the North and South Poles.
Today, wind energy
is mainly used to generate electricity. Wind is called a renewable energy
source because the wind will blow as long as the sun
shines.
The History of
Wind
Since ancient
times, people have harnessed the winds energy. Over 5,000 years ago, the
ancient Egyptians used wind to sail ships on the Nile River. Later, people
built windmills to grind wheat and other grains. The earliest known
windmills were in Persia (Iran). These early windmills looked like large
paddle wheels. Centuries later, the people of Holland improved the basic
design of the windmill. They gave it propeller-type blades, still made
with sails. Holland is famous for its windmills.
American colonists
used windmills to grind wheat and corn, to pump water, and to cut wood at
sawmills. As late as the 1920s, Americans used small windmills to generate
electricity in rural areas without electric service. When power lines
began to transport electricity to rural areas in the 1930s, local
windmills were used less and less, though they can still be seen on some
Western ranches.
The oil shortages
of the 1970s changed the energy picture for the country and the world. It
created an interest in alternative energy sources, paving the way for the
re-entry of the windmill to generate electricity. In the early 1980s wind
energy really took off in California, partly because of state policies
that encouraged renewable energy sources. Support for wind development has
since spread to other states, but California still produces more than
twice as much wind energy as any other state.
The first offshore
wind park in the United States is planned for an area off the coast of
Cape Cod, Massachusetts (read an article about the Cape Cod Wind Project).
HOW WIND MACHINES
WORK
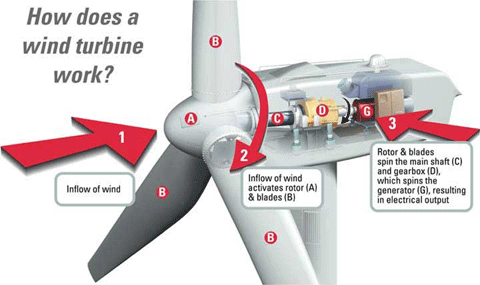
Like old fashioned
windmills, today’s wind machines use blades to collect the wind’s kinetic
energy. Windmills work because they slow down the speed of the wind. The
wind flows over the airfoil shaped blades causing lift, like the effect on
airplane wings, causing them to turn. The blades are connected to a drive
shaft that turns an electric generator to produce electricity.
With the new wind
machines, there is still the problem of what to do when the wind isn’t
blowing. At those times, other types of power plants must be used to make
electricity.
TYPES OF WIND
MACHINES
There are two
types of wind machines (turbines) used today based on the direction of the
rotating shaft (axis): horizontal–axis wind machines and vertical-axis
wind machines. The size of wind machines varies widely. Small turbines
used to power a single home or business may have a capacity of less than
100 kilowatts. Some large commercial sized turbines may have a capacity of
5 million watts, or 5 megawatts. Larger turbines are often grouped
together into wind farms that provide power to the
electrical grid.
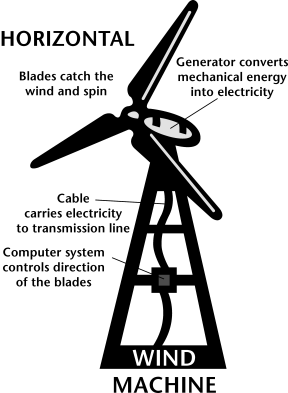
Horizontal-axis
Most wind machines
being used today are the horizontal-axis type. Horizontal-axis wind
machines have blades like airplane propellers. A typical horizontal wind
machine stands as tall as a 20-story building and has three blades that
span 200 feet across. The largest wind machines in the world have blades
longer than a football field! Wind machines stand tall and wide to capture
more wind.
Vertical-axis
Vertical–axis wind
machines have blades that go from top to bottom and the most common type
(Darrieus wind turbine) looks like a giant two-bladed egg beaters. The
type of vertical wind machine typically stands 100 feet tall and 50 feet
wide. Vertical-axis wind machines make up only a very small percent of the
wind machines used today.
The Wind Amplified
Rotor Platform (WARP) is a different kind of wind system that is designed
to be more efficient and use less land than wind machines in use today.
The WARP does not use large blades; instead, it looks like a stack of
wheel rims. Each module has a pair of small, high capacity turbines
mounted to both of its concave wind amplifier module channel surfaces. The
concave surfaces channel wind toward the turbines, amplifying wind speeds
by 50 percent or more. Eneco, the company that designed WARP, plans to
market the technology to power offshore oil platforms and wireless
telecommunications systems.
WIND POWER
PLANTS

Wind power
plants, or wind farms as they are sometimes
called, are clusters of wind machines used to produce
electricity. A wind farm usually has dozens of
wind machines scattered over a large area. The world's
largest wind farm, the Horse Hollow Wind Energy Center in
Texas, has 421 wind turbines that generate enough electricity to
power 230,000 homes per year.
Unlike power plants, many
wind plants are not owned by public utility companies. Instead
they are owned and operated by business people who sell the
electricity produced on the wind farm to electric
utilities. These private companies are known as Independent Power
Producers.
Operating
a wind power plant is not
as simple as just building a
windmill in a windy place. Wind
plant owners must carefully plan where to
locate their machines. One important thing to consider is how fast
and how much the wind blows.
|
As a rule, wind
speed increases with altitude and over open areas with no windbreaks.
Good sites for wind plants are the tops of smooth, rounded hills, open
plains or shorelines, and mountain gaps that produce wind funneling.
Wind speed
varies throughout the country. It also varies from season to season. In
Tehachapi, California, the wind blows more from April through October
than it does in the winter. This is because of the extreme heating of
the Mojave Desert during the summer months. The hot air over the desert
rises, and the cooler, denser air above the Pacific Ocean rushes through
the Tehachapi mountain pass to take its place. In a state like Montana,
on the other hand, the wind blows more during the winter. Fortunately,
these seasonal variations are a good match for the electricity demands
of the regions. In California, people use more electricity during the
summer for air conditioners. In Montana, people use more electricity
during the winter months for heating.
WIND
PRODUCTION
In 2005, wind
machines in the United States generated a total of 17.8 billion kWh per
year of electricity, enough to serve more than 1.6 million households.
This is enough electricity to power a city the size of Chicago, but it is
only a small fraction of the nation's total electricity production, about
0.4 percent. The amount of electricity generated from wind has been
growing fast in recent years, tripling since 1998.
New technologies
have decreased the cost of producing electricity from wind, and growth in
wind power has been encouraged by tax breaks for renewable energy and
green pricing programs. Many utilities around the country offer green
pricing options that allow customers the choice to pay more for
electricity that comes from renewable sources.
Wind machines
generate electricity in 25 different states in 2005. The states with the
most wind production are California, Texas, Iowa, Minnesota, and Oklahoma.
The United States
ranks third in the world in wind power capacity, behind Germany and Spain
and before India. Denmark ranks number five in the world in wind power
capacity but generates 20 percent of its electricity from wind. Most of
the wind power plants in the world are located in Europe and in the United
States where government programs have helped support wind power
development.
WIND AND THE
ENVIRONMENT
In the 1970s, oil
shortages pushed the development of alternative energy sources. In the
1990s, the push came from a renewed concern for the environment in
response to scientific studies indicating potential changes to the global
climate if the use of fossil fuels continues to increase. Wind energy is
an economical power resource in many areas of the country. Wind is a clean
fuel; wind farms produce no air or water pollution because no fuel is
burned. Growing concern about emissions from fossil fuel generation,
increased government support, and higher costs for fossil fuels
(especially natural gas and coal) have helped wind power capacity in the
United States grow substantially over the last 10 years.
The most serious
environmental drawbacks to wind machines may be their negative effect on
wild bird populations and the visual impact on the landscape. To some, the
glistening blades of windmills on the horizon are an eyesore; to others,
they’re a beautiful alternative to conventional power plants.
Last Revised: August 2008
Sources: Energy
Information Administration, Renewable Energy Trends 2005,
September 2004.
The National Energy Education Development Project,
Intermediate Energy Infobook, 2005.
The American Wind
Association, , 2007.
The Global Wind Energy Council , April
2007.
FPL Energy , September 2006.
U.S. Department of Energy,
Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy May 2007.
New- Our new 5kw to
50kw has a new technique called
"Adjustable-Pitch",
this means the wind turbine blades will change degree when the
wind speed is higher, (over the rated wind speed) keeping the wind
turbines always within their rated wind speed. The technique is far
more advanced then our old wind turbines and others being manufactured in
the world today. Atlantis Solar and Wind now backs our wind turbines up
with a 50 Year Warranty. Atlantis Solar and Wind Co. is America's and China’s leading
supplier of small to large wind turbines. Our mission is to demonstrate
green energy is a genuinely viable proposition whether on or off
the electrical grid and that renewable energy systems represent sound
financial and environmental investments in our future. Our products are
not only used in USA and China, but also exported to South East Asia,
Ireland, Canada etc illustrating the rapid global acceptance of our
products based on advanced technological design, continuous development
and state of the art manufacturing processes.
Atlantis Solar and Wind
has benefited from extensive Government recognition and support,
accelerating market demand for renewable energy and a comprehensive after
sales support program. We continuously research and develop improvements
in our small turbines in the areas of technical performance, manufacturing
quality and reliability and cost to further increase our market position
and competitiveness.
1. Wind
Generator
Principle: Use the wind energy as the motive power to revolve
a permanent-magnet generator at low speed to generate alternate current,
which is converted to direct current through constant-voltage rectifier
under control and stored in the battery. The direct current transmitted
from the battery can be converted to alternate current through inversion
power source and then put into use by linking to
load.
Features: The product is featured by novel
design, unique technique and strong practicability. The key technique of
the unit has been awarded the invention patent and practical new patent by
the State Intellectual Property Office and enjoys the independent
intellectual property right in our country. The product takes the lead at
home in the wind energy-electric energy conversion efficiency technique.
Compared with its counterparts, it has a lower rated revolving speed, thus
raising the work efficiency.
Application: The product is used in the areas with wind and
without electricity such as: island, desert, plain, beach, frontier
defense, microwave communication, telephone transmitting tower, forest
observation tower, maintenance station of oil delivery pipeline, lighting
of expressway, and etc. It is also used in the areas with wind and with
out electricity such as lighting for square, park, the place of urban
landscape point, scenery resorts, lighting for highway, ecological in
village etc. According to require can connect with nation electrified wire
netting, use wind electricity with wind, and use net electricity without
wind. It can view and admire also utilize wind energy generate that it
without any cost, save energy resources for country.
Off-Grid
Wind Power System
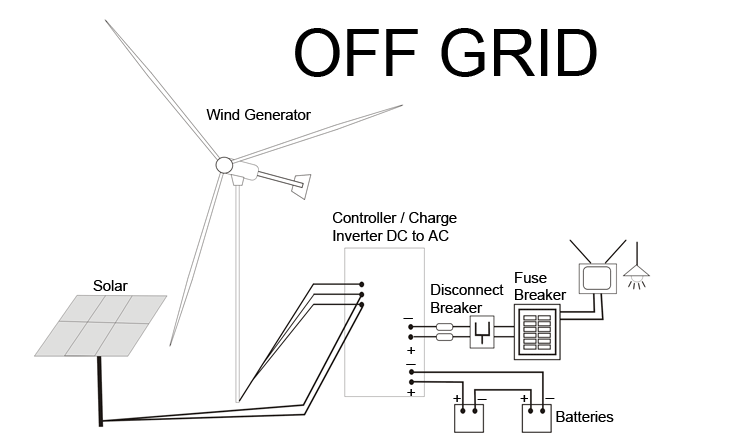
On-Grid Wind
Power System
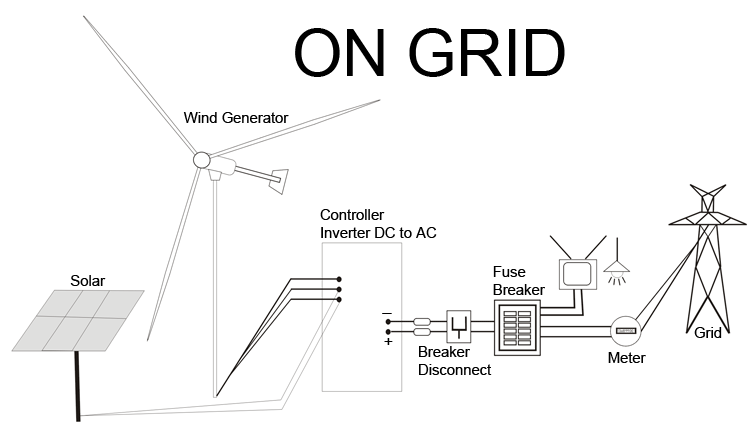
|
1.1.
200W Wind Generator
(Model Number:
FD2.1-200-8)
Technical
Parameter
|
| RATED POWER |
200W |
| MAX POWER |
300W |
| OUTPUT DC
VOLTAGE |
12V / 24V |
| CUT-IN WIND
SPEED |
3m/s |
| RATED WIND
SPEED |
6m/s |
| MAX WIND
SPEED |
40m/s |
| Cut-Out Wind
Speed |
None |
| Blade Pitch
Control |
None, Fixed
Pitch |
| Overspeed
Protection |
Auto Furl |
| Gearbox |
None, Direct
Drive |
| Temperature
Range |
-40 to +60 Deg. C (-40 to
+140 Deg. F) |
| ROTOR
Diameter |
2.20m |
| Rotor speed |
450rpm |
| blade |
3 |
| Blade
material |
Reinforced fiber
glass |
| Height of
tower |
4.5m |
| Generator |
3
phase permanent magnet alternator |
| Sine Inverter power
output |
AC 110/220V,
50HZ/60HZ |
| Weight |
85
kg | |
1.2.
300W Wind Generator
(Model Number:
FD2.5-300-8)
Technical
Parameter
|
| RATED
POWER |
300W |
| MAX
POWER |
400W |
| OUTPUT
DC VOLTAGE |
12V /
24V |
| CUT
IN WIND SPEED |
3m/s |
| RATED
WIND SPEED |
7m/s |
| MAX
WIND SPEED |
40m/s |
| Cut-Out Wind
Speed |
None |
| Blade
Pitch Control |
None,
Fixed Pitch |
| Overspeed
Protection |
Auto
Furl |
| Gearbox |
None,
Direct Drive |
| Temperature
Range |
-40 to
+60 Deg. C (-40 to +140 Deg. F) |
| ROTOR
Diameter |
2.50m |
| Rotor
speed |
400rpm |
| blade |
3 |
| Blade
material |
Reinforced fiber
glass |
| Height
of tower |
6.0m |
| Generator |
3
phase permanent magnet alternator |
| Sine
Inverter power output |
AC
110/220V, 50HZ/60HZ |
| Weight |
105
kg |
|
1.3. 500W Wind
Generator
(Model Number:
FD2.7-500-10)
Technical
Parameter
|
| RATED
POWER |
500W |
| MAX
POWER |
700W |
| OUTPUT
DC VOLTAGE |
24V /
36V |
| CUT
IN WIND SPEED |
3m/s |
| RATED
WIND SPEED |
8m/s |
| MAX
WIND SPEED |
40m/s |
| Cut-Out Wind
Speed |
None |
| Blade
Pitch Control |
None,
Fixed Pitch |
| Overspeed
Protection |
Auto
Furl |
| Gearbox |
None,
Direct Drive |
| Temperature
Range |
-40 to
+60 Deg. C (-40 to +140 Deg. F) |
| ROTOR
Diameter |
2.70m |
| Rotor
speed |
400rpm |
| blade |
3 |
| Blade
material |
Reinforced fiber
glass |
| Height
of tower |
6.0m |
| Generator |
3
phase permanent magnet alternator |
| Sine
Inverter power output |
AC
110/220V, 50HZ/60HZ |
| Weight |
125
kg | |
1.4. 1kW Wind
Generator
(Model Number:
FD3.0-1000-10)
Technical
Parameter
|
|
RATED
POWER |
1KW |
|
MAX POWER |
1.5KW |
|
OUTPUT DC
VOLTAGE |
48V |
|
CUT IN WIND
SPEED |
3m/s |
|
RATED WIND
SPEED |
9m/s |
|
MAX WIND
SPEED |
40m/s |
|
Cut-Out Wind
Speed |
None |
|
Blade Pitch
Control |
None, Fixed
Pitch |
|
Overspeed
Protection |
Auto
Furl |
|
Gearbox |
None, Direct
Drive |
|
Temperature
Range |
-40 to +60 Deg. C (-40 to
+140 Deg. F) |
|
ROTOR
Diameter |
3.10m |
|
Rotor
speed |
400rpm |
|
blade |
3 |
|
Blade
material |
Reinforced fiber
glass |
|
Weight of
blade |
15 kg |
|
Height of
tower |
6.0m |
|
Weight of
tower |
60 kg |
|
Diameter of tower
pipe |
114 mm |
|
Weight of
turbine |
42 kg |
|
Generator |
3 phase permanent magnet
alternator |
|
Sine Inverter power
output |
AC 110/220V,
50HZ/60HZ |
|
Weight |
180
kg | |
1.5. 2kW Wind
Generator
(Model Number:
FD3.6-2000-10)
|
|

|
Technical
Parameter
|
| RATED POWER |
2KW |
| MAX POWER |
2.6KW |
| OUTPUT DC
VOLTAGE |
220-300V |
| CUT IN WIND
SPEED |
3m/s |
| RATED WIND
SPEED |
9m/s |
| MAX WIND
SPEED |
40m/s |
| Cut-Out Wind
Speed |
None |
| Blade Pitch
Control |
None,
Fixed Pitch |
| Over Speed
Protection |
Auto
Furl |
| Gearbox |
None,
Direct Drive |
| Temperature
Range |
-40 to
+60 Deg. C (-40 to +140 Deg. F) |
| ROTOR
Diameter |
3.70m |
| Rotor speed |
400rpm |
| blade |
3 |
| Blade
material |
Reinforced fiber
glass |
| Weight of
blade |
18
kg |
| Height of
tower |
9.0m |
| Weight of
tower |
120
kg |
| Diameter of tower
pipe |
140
mm |
| Weight of
turbine |
52
kg |
| Generator |
3
phase permanent magnet alternator |
| Sine Inverter power
output |
AC
110/220V, 50HZ/60HZ |
| Weight |
270
kg |
| Functional
Features |
Low-End Boost, Slow-Mode,
Brake | |
1.6. 3kW Wind
Generator
(Model Number:
FD5.0-3000-16)
Technical
Parameter
|
| RATED
POWER |
3KW |
| MAX
POWER |
3.3KW |
| OUTPUT
DC VOLTAGE |
220-300V |
| CUT IN
WIND SPEED |
3m/s |
| RATED
WIND SPEED |
10m/s |
| MAX
WIND SPEED |
40m/s |
| Cut-Out Wind
Speed |
None |
| Blade
Pitch Control |
None,
Fixed Pitch |
| Over
Speed Protection |
Auto
Furl |
| Gearbox |
None,
Direct Drive |
| Temperature
Range |
-40 to
+60 Deg. C (-40 to +140 Deg. F) |
| ROTOR
Diameter |
5m |
| Rotor
speed |
400rpm |
| blade |
3 |
| Blade
material |
Reinforced fiber
glass |
| Weight
of blade |
34.5
kg |
| Height
of tower |
9.0m |
| Weight
of tower |
597
kg |
| Diameter of tower
pipe |
273
mm |
| Weight
of turbine |
152
kg |
| Generator |
3
phase permanent magnet alternator |
| Sine
Inverter power output |
AC
110/220V, 50HZ/60HZ |
| Weight |
941.5
kg |
| Functional
Features |
Low-End Boost, Slow-Mode,
Brake | |
1.7. 5kW Wind
Generator
(Model Number:
FD6.4-5000-16)
Technical
Parameter
|
|

|
| RATED
POWER |
5
KW |
| MAX
POWER |
8
KW |
| OUTPUT
VOLTAGE |
280
V |
| START
WIND SPEED |
2
m/s |
| RATED
WIND SPEED |
10
m/s |
| Blade
Pitch Control |
None,
Fixed Pitch |
| Overspeed
Protection |
Auto
Furl |
| Gearbox |
None,
Direct Drive |
| Temperature
Range |
-40 to
+60 Deg. C (-40 to +140 Deg. F) |
| ROTOR
Diameter |
6.40m |
| Rotor
speed |
200rpm |
| blade |
3 |
| Blade
material |
Reinforced fiber
glass |
| Height
of tower |
12m |
| Generator |
3
phase permanent magnet alternator |
| Sine
Inverter power output |
AC
110/220V, 50HZ/60HZ |
| Functional
Features |
Low-End Boost, Slow-Mode,
Brake | |
1.8. 10kW Wind
Generator
(Model Number:
FD8.0-10Kw-20)
|
|

|
Technical
Parameter
|
| RATED POWER |
10 KW |
| MAX POWER |
12 KW |
| OUTPUT
VOLTAGE |
280/420V |
| START WIND
SPEED |
2 m/s |
| RATED WIND
SPEED |
10 m/s |
| Cut-Out Wind
Speed |
None |
| Blade Pitch
Control |
None, Fixed
Pitch |
| Overspeed
Protection |
Auto programme
control |
| Gearbox |
None, Direct
Drive |
| Temperature
Range |
-40 to +70 Deg.
C |
| ROTOR
Diameter |
8.00m |
| Rotor speed |
200rpm |
| Blade |
3 |
| Blade
material |
Reinforced fiber
glass |
| Weight of
blade |
96 kg |
| Height of
tower |
12m |
| Weight of
tower |
666 kg |
| Diameter of tower
pipe |
325 mm |
| Weight of
turbine |
392 kg |
| Generator |
3 phase permanent magnet
alternator |
| Sine Inverter power
output |
AC 220/380V,
50HZ/60HZ |
| Functional
Features |
Slow-Mode,
Brake | |
1.9. 20kW Wind
Generator
(Model Number:
FD12-20kw-40-3)
Technical
Parameter
|
|

|
| RATED POWER |
20
KW |
| MAX POWER |
22
KW |
| OUTPUT
VOLTAGE |
420
V |
| START WIND
SPEED |
2
m/s |
| RATED WIND
SPEED |
12
m/s |
| Cut-Out Wind
Speed |
None |
| Blade Pitch
Control |
None,
Fixed Pitch |
| Overspeed
Protection |
Auto
programme control |
| Gearbox |
None,
Direct Drive |
| Temperature
Range |
-40 to
+70 Deg. C |
| ROTOR
Diameter |
12.00m |
| Rotor speed |
160
rpm |
| blade |
3 |
| Length of
Blade |
600
cm |
| Width of
Blade |
60
cm |
| Thickness of
Blade |
23
cm |
| Blade
material |
Reinforced fiber
glass |
| Height of
tower |
18
m |
| Generator |
3
phase permanent magnet alternator |
| Sine Inverter power
output |
AC
220/380V, 50HZ/60HZ |
| Functional
Features |
Slow-Mode,
Brake | |
2. Small Wind
Power Inverter
|
|

|
3.
Small Wind Turbine Grid-connected
Converter
|
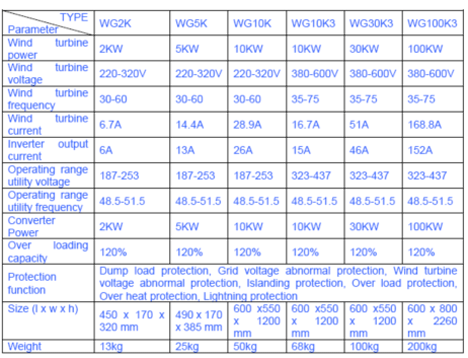
Small wind turbine grid-connected
power system includes small wind turbine dump load, grid
-connected inverter, meter and power switchboard. When
wind speed reaches the cut-in-speed, the AC power from
the wind turbine will be fed in the utility grid after
rectifying and inverting. If the wind speed is too
large, part of the dump load will be connected to the
wind turbine to keep the constant power to feed in the
utility grid.
|
Product
advantages
*DSP
controller
*MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking)
technology;
*High efficiency up to 95%;
*Perfect
protect functions include anti-islanding;
I*n
accordance with IEEE929-2000,UL174;
*Quick and easy
installation;
*A LCD display for monitoring all
system information;
*Can set the operation
parameters via LCD and keys;
* Boost circuit
provide wide AC input range;
*Mitsubishi IPM Module
inside;
*Electrical
brake.
Technical
Parameter
|
|
|
|

|
4. Wind
Turbine Blades
We have
developed and manufactured wind turbine blades and other
composite parts for wind power generator since
1996.
|
The blades are the main parts
of wind power generator. In future most of the blades
will be made of FRP or CRP composites. It includes
the following in structure:
1.Root: made of
metal.
2. Shell: made of composite.
3.
Strengthen part: Made of glass or carbon fiber
composites.
Now we have the capacity to manufacture
the blades whose diameter is from 2-48 meters (rated
power 100w-600KW). Some of the wind turbine blade served
for domestic wind power generator, and most of them have
shipped through out America, China, Denmark, Germany,
Korea, India and
Japan.
| | | |





![]()
 WebMaster
WebMaster![]()